What is Labelling?
Labelling is an essential aspect of product packaging, involving the attachment of informative tags or stickers to products or their packaging. These labels convey crucial details about the product and its manufacturer.
Labelling serves to provide brand identification, describe the product’s contents, promote the product, categorize it into different grades, protect consumers from deceptive practices, ensure legal compliance, and facilitate the buying process.
It includes various types of labels, such as brand labels, grade labels, and descriptive labels, each serving specific purposes. In essence, labeling is a vital tool in the marketplace for product identification, promotion, and consumer protection.
What is a Product Label?
A product label is a concise informational element affixed to a product or its packaging. It serves to identify the brand, convey product details, and fulfill legal requirements. Product labels typically include brand information, a description of the product’s contents, marketing messages or promotions, legal information like certifications, company contact details, and identification marks such as UPC codes.
These labels are crucial for both manufacturers and consumers, aiding in product recognition, differentiation, and informed decision-making. They play a pivotal role in conveying essential product information and facilitating the buying process in various industries.
Types of Labelling
Generally, there are three types of product labels – brand label, grade label, and informational label.
Brand Labels
Brand labels primarily focus on promoting and differentiating the product by highlighting the brand name, logo, and trademark. They aim to create brand recognition and loyalty among consumers.
Example: Coca-Cola’s label, which prominently displays its brand name and iconic red logo, is a classic example. The label’s purpose is to ensure consumers can easily identify and choose the Coca-Cola brand among other soft drinks.
Read More: Brand Equity – Definition
Grade Labels
Grade labels are used to classify products based on quality or grade. They help consumers and intermediaries differentiate between various grades of a product, making it easier to make informed purchasing decisions.
Example: In the tea industry, grade labels like “Green Tea,” “Tea Bags,” or “Leaf Tea” categorize tea products based on their quality or type. These labels assist consumers in choosing the specific tea they prefer.
Informational Labels
Informational labels provide detailed product information, including ingredients, usage instructions, nutritional facts, expiration dates, and more. They are essential for products where consumers require comprehensive information.
Example: Medicines and cosmetics often feature informational labels, offering details on usage, ingredients, warnings, and more. For instance, a sunscreen product label includes information about SPF, usage, and potential skin sensitivity warnings.
Read More: 10 Key Functions of Packaging in Marketing
Functions of Labelling
Product labeling plays a crucial role in informing consumers, marketing products, and complying with legal requirements. Here are seven essential functions of product labeling:
Product Identification
Labeling serves as the primary means to make products easily identifiable. It enables customers to recognize the product and its brand. This identification is crucial in crowded marketplaces where various similar products are available. For example, a recognizable label ensures that customers can quickly distinguish between different brands of soft drinks or canned goods.
Grading
Labels help categorize products into different grades or quality levels. This grading system allows consumers to understand the quality of the product they are purchasing. For instance, labels on electronic gadgets may indicate product specifications or performance grades, helping consumers make informed choices.
Consumer Protection
Labels provide consumers with vital information about the product, including its contents, usage instructions, safety precautions, and potential allergens. This information protects consumers from deceptive or fraudulent practices by sellers. For instance, food labels indicate nutritional information and allergy warnings, ensuring consumers can make informed and safe choices.
Read More: 5 Essentials of Good Packaging
Legal Compliance
Labels are necessary to meet legal requirements. Many countries have specific regulations that products must adhere to, such as providing accurate information about the product, including ingredients, quality certifications, and statutory warnings. For example, tobacco products must carry statutory health warnings on their labels.
Marketing and Promotion
Labels are a valuable marketing tool. They serve as an advertising medium, allowing brands to display attractive graphics, promotional messages, and offers. Eye-catching labels can draw customers’ attention and encourage them to make a purchase. For example, labels may include special offers like “Buy One, Get One Free” or “Limited Time Discount.”
Facilitating Purchasing Decisions
A well-designed label helps customers make purchasing decisions. Labels provide essential information about the product, including price, quantity, quality, and usage instructions. Customers can quickly compare products based on the information provided, enabling them to make choices that align with their specific requirements.
Read More: 10 Importance of Product Packaging
Encouraging Self-Service
Labels play a significant role in self-service retail environments. In large departmental stores and supermarkets, labels provide customers with information about product ingredients, pricing, quantity, and usage instructions. This empowers customers to make informed purchasing decisions without requiring assistance from sales staff.
Components of a Label
Components of a label typically include the following six. These components collectively serve to provide information, market the product, meet legal requirements, and enhance brand recognition, offering a comprehensive view of the product for both businesses and consumers.

- Brand Information: This part of the label conveys information about the brand, including the brand name, logo, tagline, and brand message. It helps in product differentiation and brand recognition.
- Product Description: The label includes essential information about the product, such as its contents, ingredients, weight, size, and usage instructions. This section provides clarity about the product itself.
- Marketing Information: Labels often serve as a marketing touchpoint, communicating promotional messages, offers, and discounts. Attractive illustrations and text align with marketing strategies to entice customers.
- Legal Information: Different industries and countries have specific legal requirements for product labels. This component includes certifications, grading, allergy information, nutrition facts, and statutory warnings as necessary.
- Company Information: Labels include information about the parent company or manufacturer, such as the company’s name, address, contact details, and location. This facilitates customer contact and accountability.
- Identification Marks: In the case of products sold in stores (online or offline), labels often include UPC codes or barcodes. These marks aid in product identification and billing processes, ensuring smooth transactions.
Read More: 10 Strategies For Product Packaging
Factors Affecting Product Labelling
Several factors influence product labeling, impacting how information is presented to consumers. Here are six key factors to mention:
Legal Regulations
Legal requirements and regulations play a significant role in shaping product labels. Different industries and regions have specific rules regarding what information must be included on labels. This includes safety warnings, nutritional facts, ingredient lists, and more. Non-compliance can lead to legal issues and product recalls.
Industry Standards
Each industry may have its own standards for labeling. These standards ensure consistency and transparency within the sector. For example, food labeling standards may dictate how nutritional information is presented, while the textile industry may have standards for fabric care labels.
Consumer Understanding
Labels should be designed with the consumer in mind. Language, symbols, and graphics should be easily understandable by the target audience. Complex jargon or obscure symbols can confuse consumers and impact purchasing decisions.
Read More: Product Life Cycle (PLC): Definition, Stages, Strategies, and Examples
Branding and Marketing
Labels are an integral part of branding and marketing. The design, colors, and overall aesthetics of the label should align with the brand’s identity and marketing strategy. An eye-catching label can attract customers and differentiate a product from competitors.
Product Specifics
The nature of the product itself affects labeling. Perishable goods may require clear expiration dates, while chemicals need detailed safety information. Labels should convey information relevant to the product’s characteristics and use.
Global Market Considerations
For products intended for international markets, labels may need to accommodate multiple languages, cultural preferences, and legal requirements. Global labeling considerations ensure products are accessible and compliant in various regions.
Read more: The 4 Cs of Marketing: Customer, Cost, Convenience, and Communication
Examples of Labelling
In today’s business world, almost every company uses product labels. Here are five examples of product labels to illustrate:
Coca-Cola – Prominent Brand Label
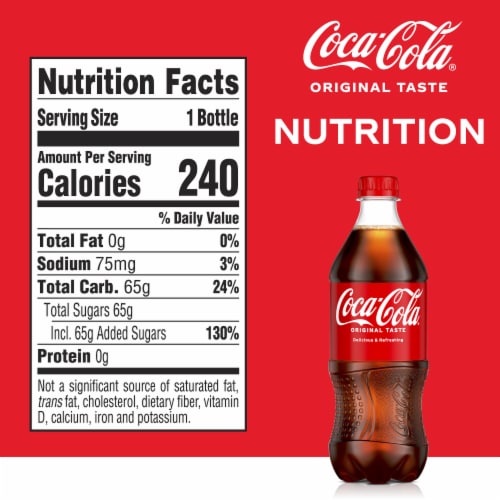
- Manufacturer: The Coca-Cola Company
- Nature: Coca-Cola is recognized for its iconic brand label, featuring the brand name, logo, and trademark. This label is an integral aspect of its packaging and serves to distinguish its products.
- Method: The Coca-Cola label is prominently displayed on its bottles and cans, instantly identifying the brand to consumers. The label’s distinct red and white design has become a global symbol of refreshment.
Lipton – Grade Label

- Company: Unilever (Lipton’s parent company)
- What: Lipton uses grade labels to indicate the quality of its tea products. These labels help consumers distinguish between various tea types and grades.
- How: Lipton’s grade labels classify its tea as “Yellow Label” and “Green Tea,” among others. These labels communicate the type and quality of tea inside the packaging, assisting consumers in making informed choices.
Prescription Medications – Descriptive and Illustrative Label
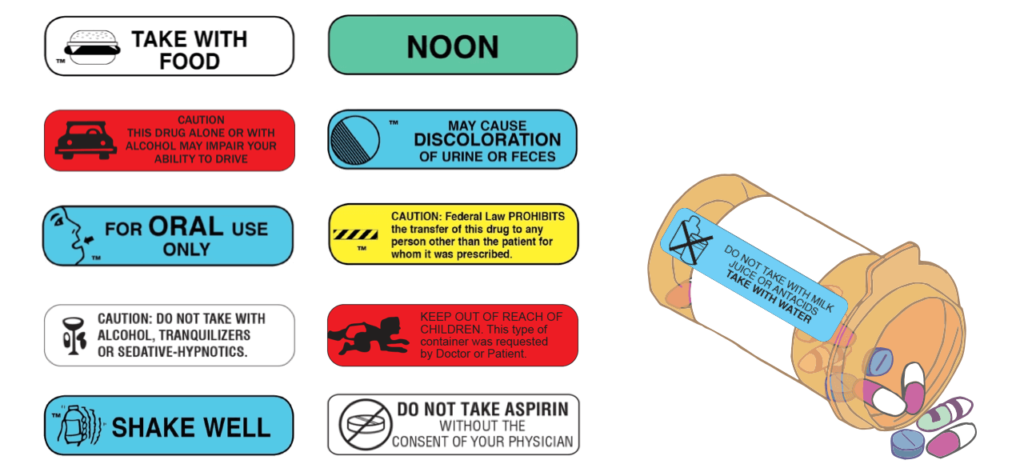
- Company: Various pharmaceutical companies
- What: Prescription medications require detailed labels with descriptive and illustrative information. These labels provide critical information about usage, dosage, side effects, and more.
- How: Pharmaceutical labels include extensive information such as the drug’s name, dosage instructions, active ingredients, warnings, and expiration dates. Illustrations may be used to clarify usage, making them vital for patient safety.
Nutritional Facts – Food Packaging
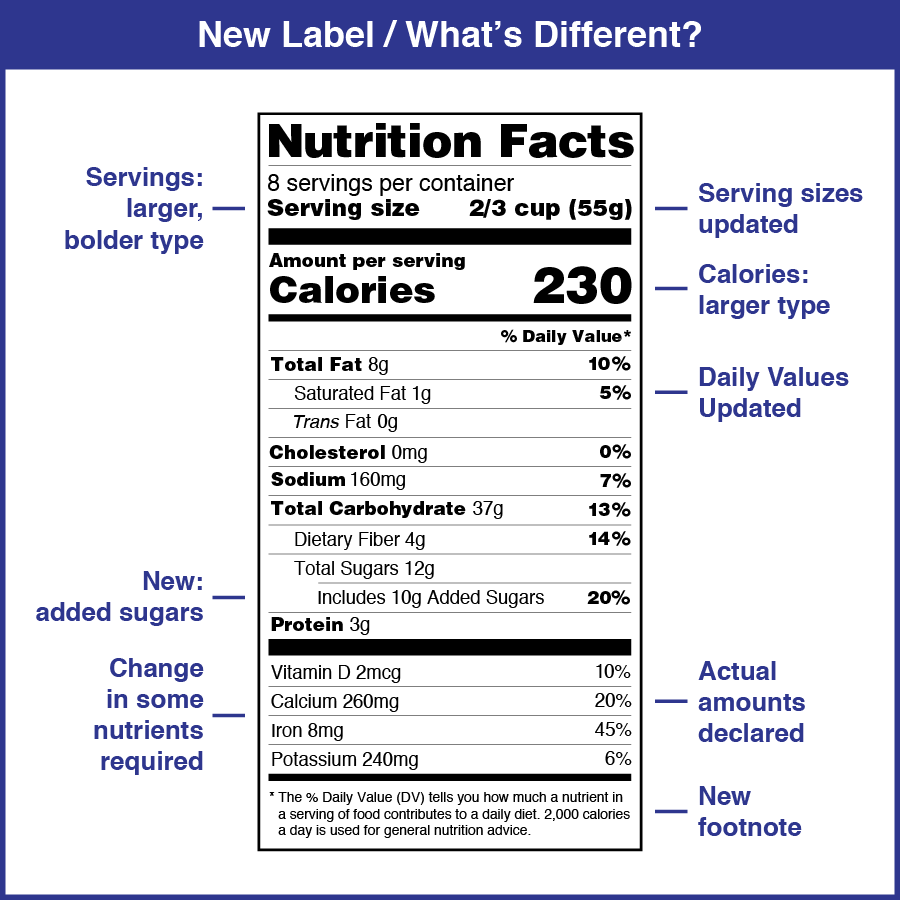
- Company: Food manufacturers
- What: Food products typically feature labels containing nutritional facts. These labels inform consumers about the product’s nutritional content.
- How: Food labels list key information like serving size, calories, fat content, vitamins, and ingredients. They play a crucial role in helping consumers make healthy food choices.
Nike Shoes – Imprinted Product Labe
- Company: Nike, Inc.
- What: Nike imprints product labels directly on its shoes. These labels contain essential information about the product.
- How: Nike’s imprinted labels on its shoes include brand logos, product names, size information, and care instructions. This approach ensures that consumers have access to key details without the need for additional tags.
These examples illustrate how different types of labeling serve various purposes, from branding and product classification to providing critical information for consumer safety and informed decision-making.
Read Next: Marketing Mix – Definition, 4Ps, 7Ps, 4Cs, Strategy, and Examples
Arti Kushmi holds a BBS (Bachelor in Business Studies) degree and shares her business and marketing knowledge through this website. While not writing she will be reading and enjoying the moment.
